What you need to know
Car Park - See if the hospital offers discounted car parking nearby.
Restaurant - Ask a member of the staff on the ward to see if you are eligible for discount in the hospital restaurant.
Ronald McDonald House - A fantastic Charity, which offers accommodation to keep the family together. It is a worth a look to see if there is one close to the hospital.
CLIC Sargant - Another fantastic Charity, they organise a lot of help for the family, bringing a range of charities together. Endless support throughout your journey.
People - Don’t isolate yourself from other people on the ward. You are all going through very similar journeys. They will become your rocks and people that can relate to you, talk to and that just understand you.
Belongings – Take items from home, such as duvets to help settle in to hospital stays, pictures always brighten the bed space up and always have a pack of cards to hand.
Journey - Everyone's journey is very different, even if they have the same diagnosis. Try and not compare, easier said than done. Different people will respond to the same medication in very different ways.
Isolation - Isolation is a stressful time however, this is to protect your child and the other children on the ward. This is normally only for a short period of time.
What you need to know
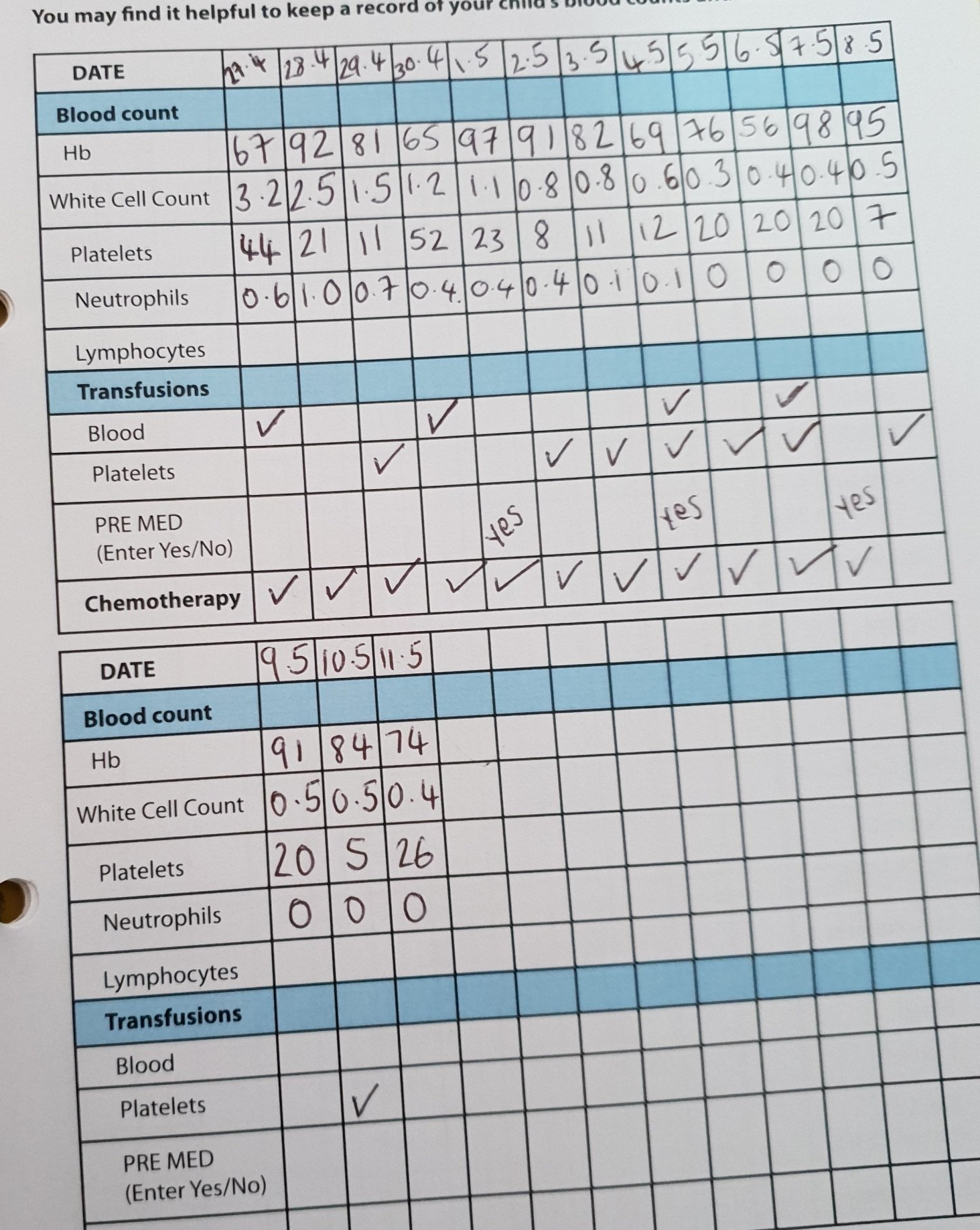
Haemoglobin - (Hb) is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. A 'Normal' level would be between 110-125
Platelets - Tiny blood cells that help your body form clots to stop bleeding. If one of your blood vessels gets damaged, it sends out signals that are picked up by platelets. A 'Normal' level would be between 150-400
White blood cells - Part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. A 'Normal' level would be between 5 - 16
Neutrophils -The most common form of white blood cell. They help the body respond to infection and heal damaged tissue. A 'Normal' level would be between 1.5 - 7
Neutropenia - Is when a person has a low level of neutrophils.
Try and track daily blood test results in your Family Journal 'Yellow book'
Children undergoing Chemotherapy will have very different blood levels compared to the 'normal' level
What you need to know
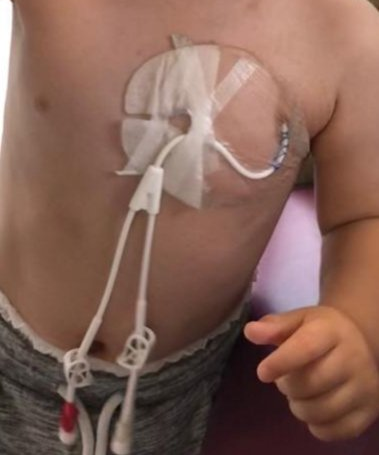
Cannula - A tube that can be inserted into the body, often for the delivery or removal of fluid.
Central venous catheter - Also known as a central line, is a catheter placed into a large vein. Catheters can be placed in veins in the neck chest, groin, or through veins in the arms (also known as a PICC line) It is used to administer medication or fluids that are unable to be taken by mouth or would harm a smaller peripheral vein, obtain blood tests .
Dressing Change -You'll need to change your dressing often, so that germs don't get into your catheter and make you sick. You should change the dressing about once a week. You will need to change it sooner if it becomes loose or gets wet or dirty. After some practice, it will get easier. A family member may be able to help you.
NG Tube - A nasogastric tube (NG Tube) is a special tube that carries food and medicine to the stomach through the nose. It can be used for all feedings or for giving a person extra calories. You'll learn to take good care of the tubing and the skin around the nostrils so that the skin doesn't get irritated.
Lumbar puncture (LP) - Also known as a spinal tap, is a medical procedure in which a needle is inserted into the spinal canal, most commonly to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for diagnostic testing.
Bone marrow aspiration - Is a procedure that involves taking a sample of the liquid part of the soft tissue inside your bones. Bone marrow is the spongy tissue found inside bones. It contains cells that produce white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets inside larger bones.
CT SCAN - Combines a series of X-ray images taken from different angles around your body and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images (slices) of the bones, blood vessels and soft tissues inside your body.
MRI SCAN - Is a type of scan that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the inside of the body.
